A staff member works at the control room of China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) in southwest China's Guizhou Province, March 27, 2021. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
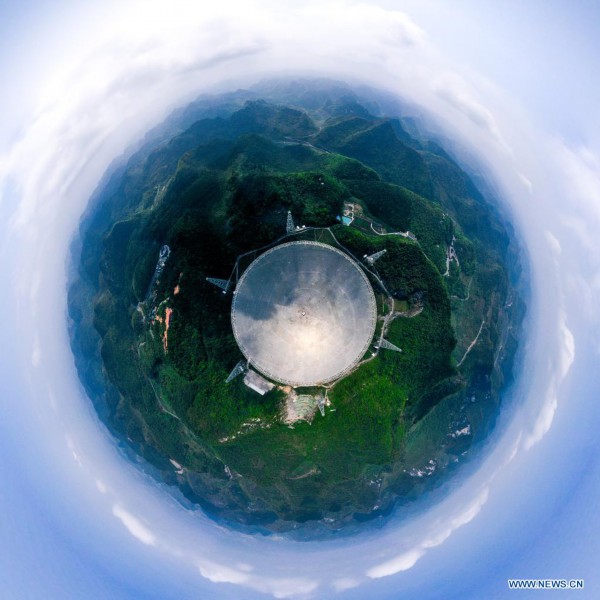

Aerial panoramic photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
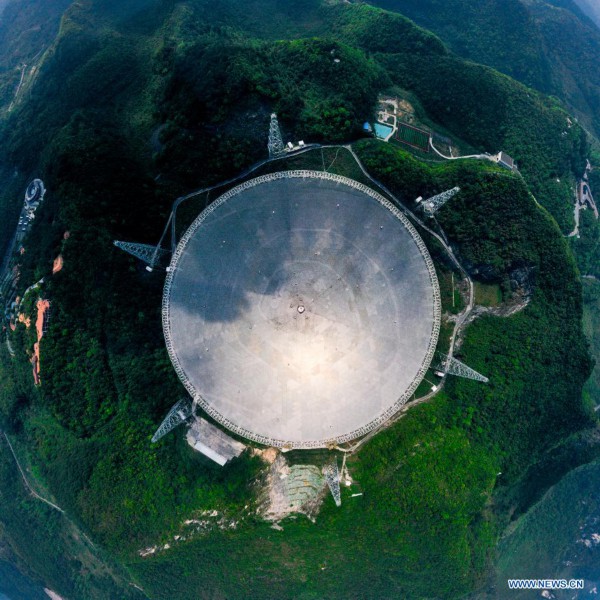

Aerial photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
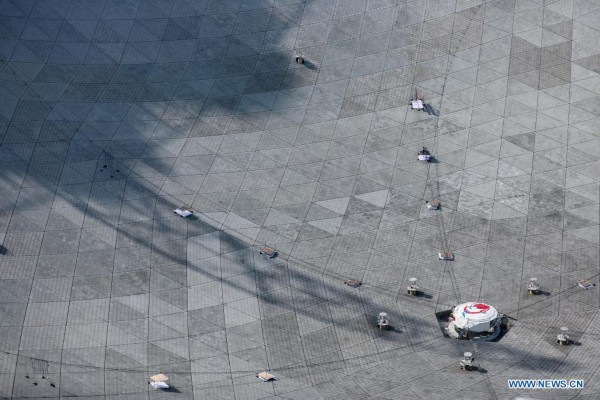

Photo taken on March 29, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
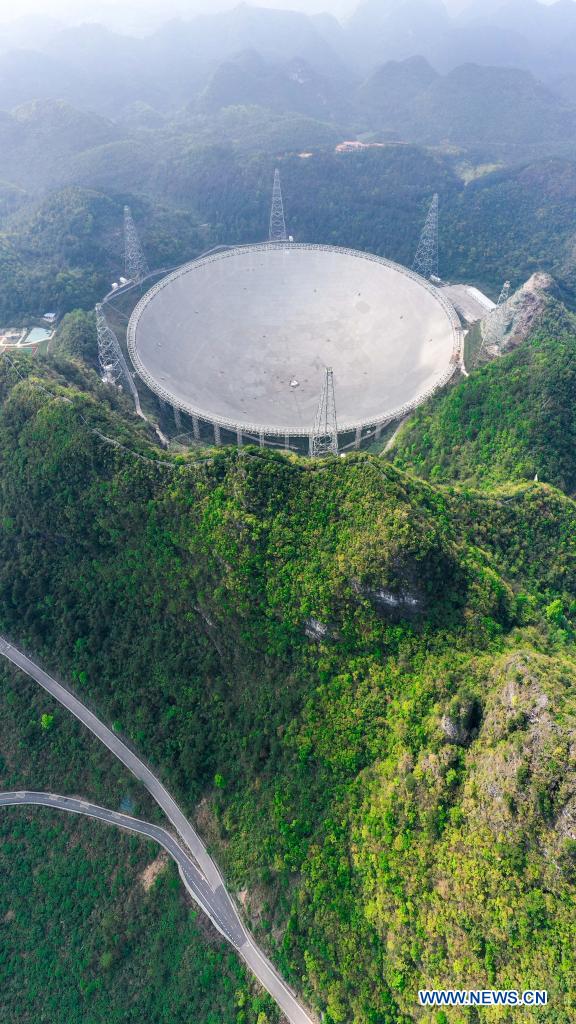

Aerial photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
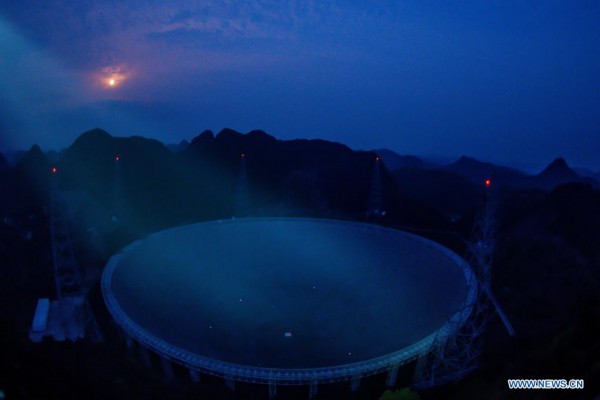

Photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
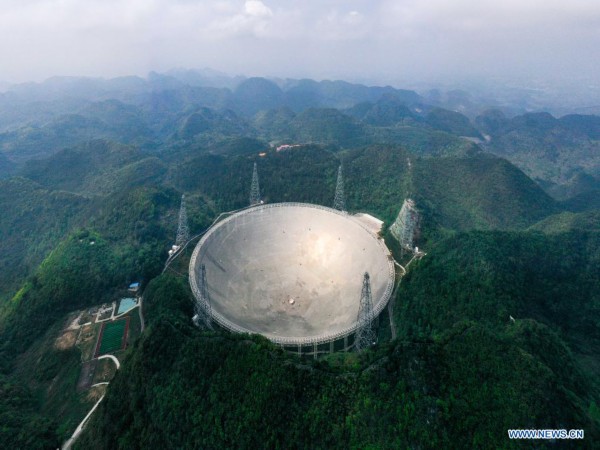

Aerial photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
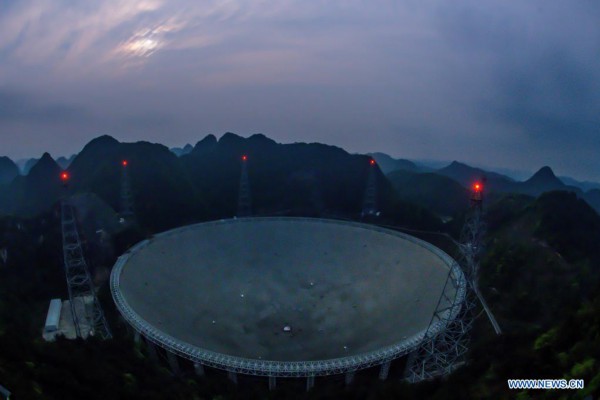

Photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
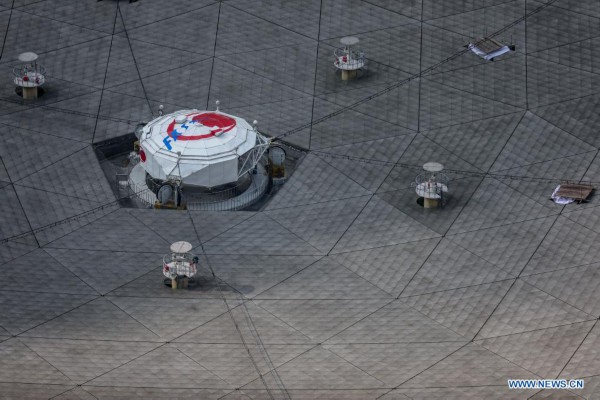

Photo taken on March 29, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
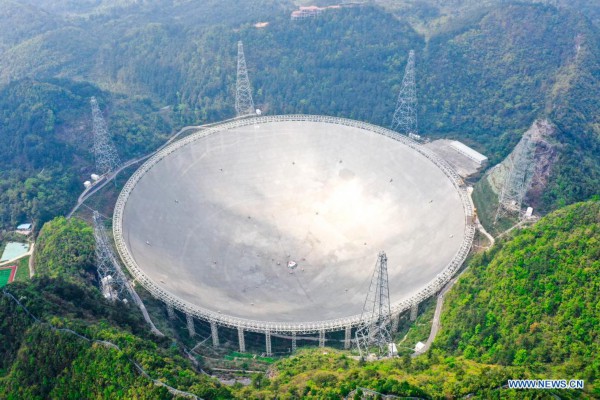

Aerial photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)

Aerial photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)

Staff members work at the control room of China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) in southwest China's Guizhou Province, March 27, 2021. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)

Aerial photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
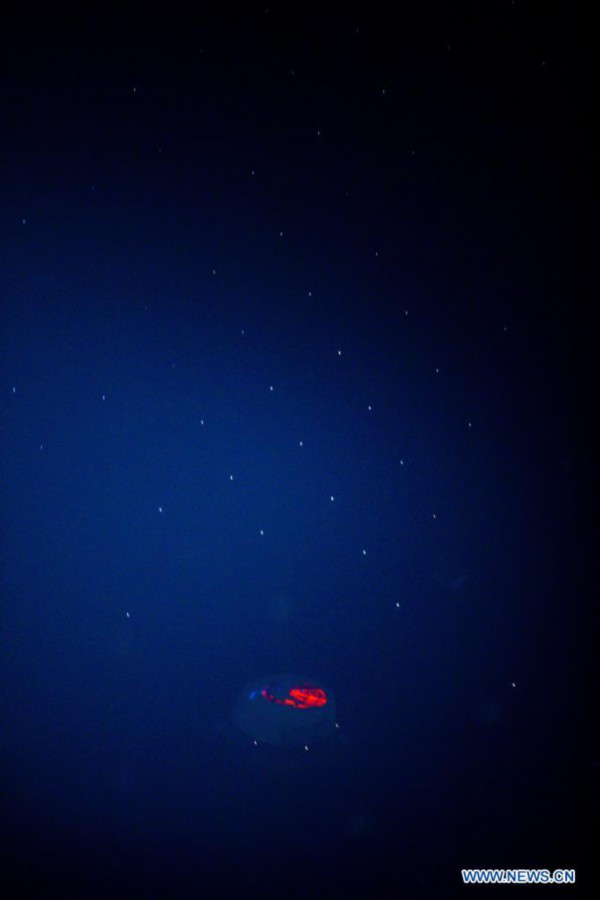

Photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
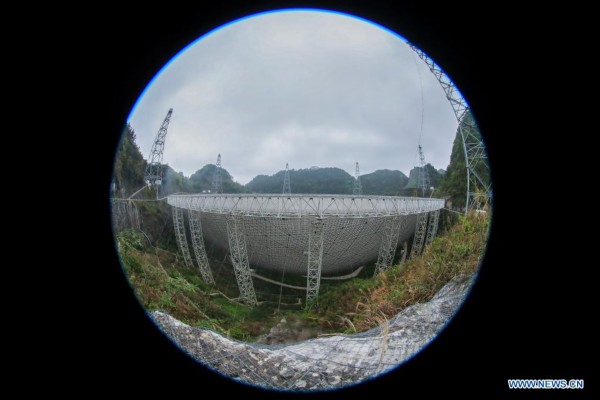

Panoramic photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
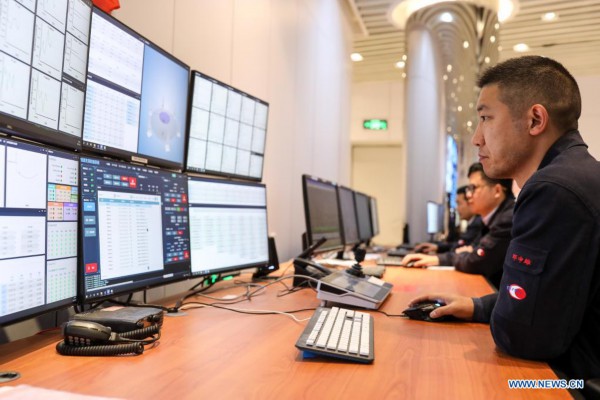

Staff members work at the control room of China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) in southwest China's Guizhou Province, March 27, 2021. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)

Aerial photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) under maintenance in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
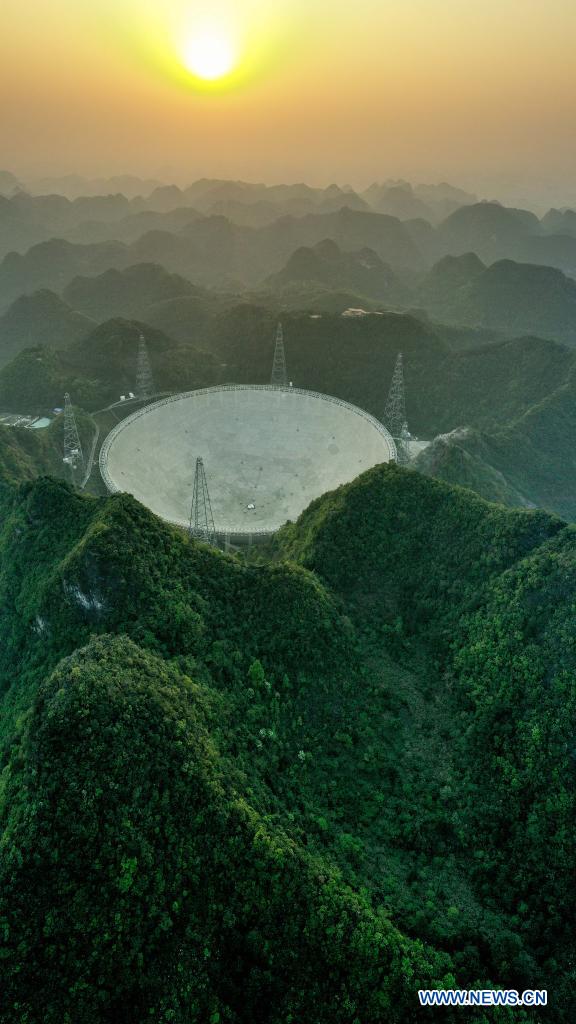

Aerial photo taken on March 29, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) at sunset in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)

Photo taken on March 29, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) at night in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)
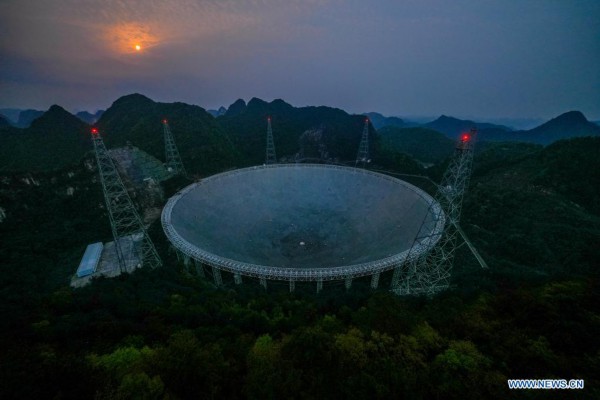

Photo taken on March 28, 2021 shows China's Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) at night in southwest China's Guizhou Province. FAST has identified over 300 pulsars so far. Located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province, it officially began operating on Jan. 11, 2020. (Xinhua/Ou Dongqu)








 公安备案号:32010202010067
公安备案号:32010202010067